FSMO stands for Flexible single master roles that help administrators perform different operations on AD. These roles are divided into forest-based or domain-based. Active Directory will not function properly without having these core roles.
5 FSMO Roles in Active Directory
Schema Master Role
It manages Read and writes a copy of the AD schema and defines all attributes. Without AD schema no one can update schema and attributes.
Domain Naming Master
It is responsible for creating or deleting a new domain name and verifying it. It also makes sure that we can’t create a second domain in the forest having the same name.
PDC Emulator
It is responsible for authenticating requests, managing GPOs, and changing passwords. It keeps track of time. It uses NTLM and Kerberos protocol to authenticate users. If the passwords have changed then it is the PDC emulator that lets the user know that the passwords have been changed.
Infrastructure Master
It is responsible for updating references from objects in the local domain to objects in other domains. The infrastructure master role compares the changes with another domain where the global catalogue is located and the changes that happened after the last visit will be replicated in other domains.
It is recommended that the Global Catalogue and Infrastructure Master roles should not be in the same place or Domain. If both are in the same domain then Infrastructure Master will not be able to change and it’ll think that everything is up to date because both are in the same place.
RIDs Master
It is responsible for allocating RIDs to DCs. The RID number is automatically assigned to every object on its creation and after that, it becomes a part of the object’s security identifier (SID) that uniquely identifies an account or group within a domain.
Priority of FSMO Roles
If there is a scenario where something went wrong in your domain controller where you have all FSMO roles then in that case we will recover the roles according to priority based. Below are the priorities of FSMO roles.
PDC > RID > Domain > Schema > Infrastructure
How to check FSMO Roles?
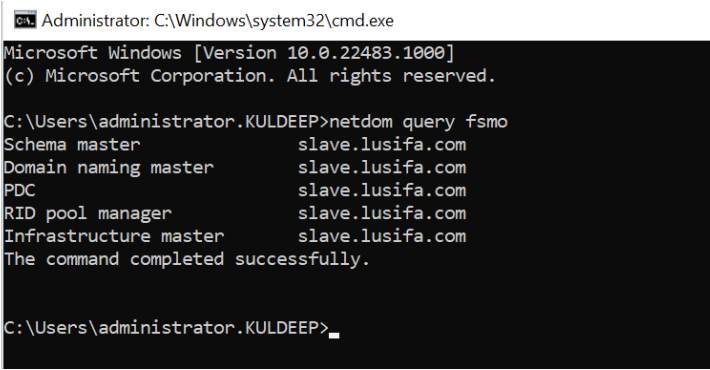
You can check the FSMO roles by entering the command netdom query fsmo and you can see the results will
Transfer FSMO Roles to another Domain Controller
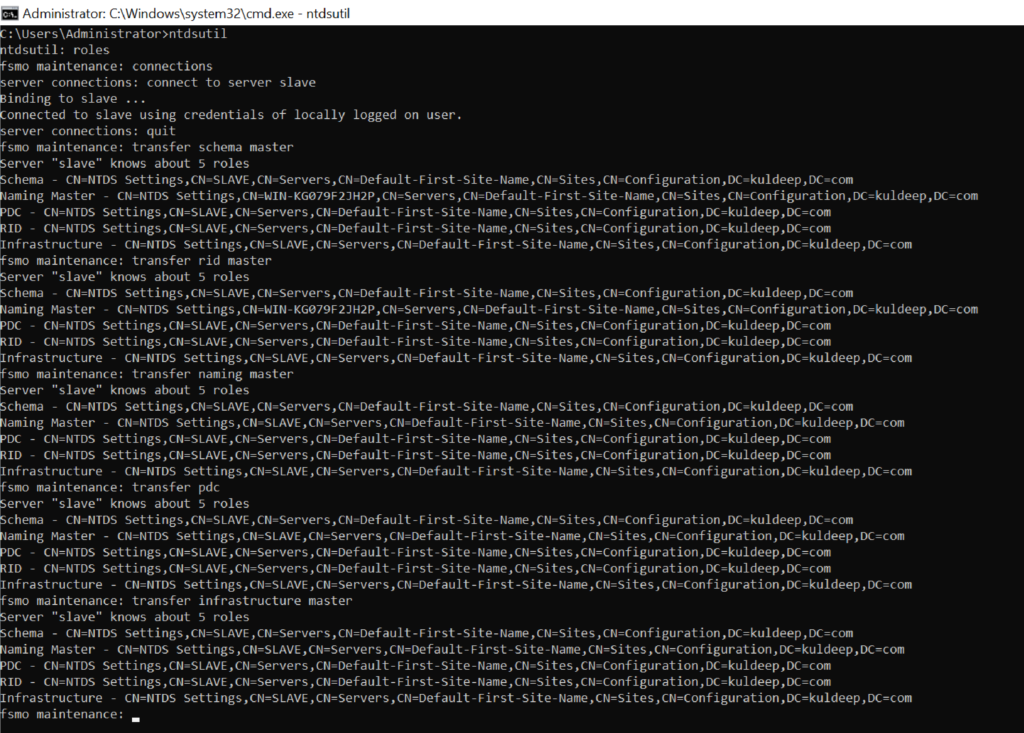
Here is the following command you can use to transfer the FSMO roles to different trusted Domain Controllers.
- Type ntdsutil and press Enter.
- Type roles and press Enter.
- Type connections and press Enter.
- Type connect to server Kuldeep and press Enter, (Where Kuldeep is the server computer name that will transfer the FSMO roles.)
- Type quit and press Enter.
- transfer schema master
- transfer rid master
- transfer naming master
- transfer PDC
- transfer infrastructure master
What is the ntdsutil command used for?
The NTDSutil.exe utility is one of the key tools to manage Active Directory and its database (ntds.dit file). Here are some use points where we mostly use the ntdsutil commands.
- Transfer (seizing) FSMO roles in the AD domain between domain controllers.
- Authoritative restoring of deleted objects in Active Directory;
- Remove faulty (missing) AD domain controllers;
- Performing AD database maintenance: checking integrity, compressing, and moving the ntds.dit file or AD log files to another drive on a domain controller in order to increase performance;
- Active Directory snapshot management.
- Change the administrator password for the DSRM (Directory Services Restore Mode) recovery mode

