Active Directory is a service developed by Microsoft for Windows domain networks. It enables administrators to manage permissions and access the network resources. Active Directory stores data as objects. An object is a single element, such as a user, group, application, or device such as a printer. It is also known as NT directory service.
What is Active Directory (AD)
AD is a collection of users, computers, and groups that are part of the same centralized system. The main service in Active Directory is Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS), which stores directory information and handles the interaction of the user domain. ADDS is also responsible for Authentication and Authorization. AD DS uses Kerberos.
Any changes to any object will immediately sync to the connected systems. AD database file NTDS.dit is based on X.500 standard.
Also Read: How to Promote a Server to a Domain Controller – A step-by-step guide – CodeRepublics
Active Directory Database
AD databases are stored on a single NTDS.dit file located in C:\Windows\NTDS
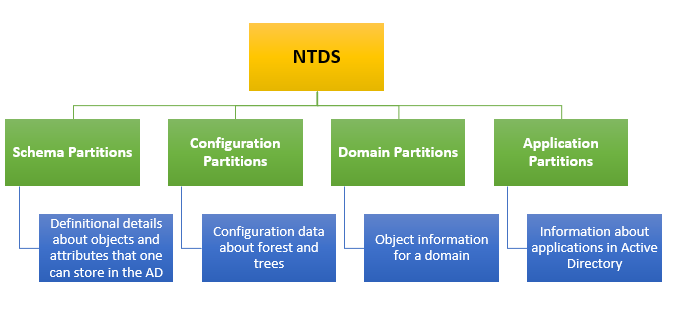
NTDS.dit file which is logically separated into the following partitions:
- Schema Partition: Defines the structure and rules for all objects and attributes in the directory. It specifies that a “user” object can have attributes like name, email, and password and Ensures consistency across the directory.
- Configuration Partition: It stores the configuration data for the entire Active Directory forest and contains information about sites, replication settings, and services. It ensures all domain controllers in the forest share the same configuration.
- Domain Partition: Contains data specific to a particular domain, such as user accounts, groups, and computers. For Example: it will store all users and devices in that domain and Manages domain-specific data.
- Application Partition: It stores data for applications or services integrated with Active Directory. Example: DNS zone data when DNS is integrated with AD. It provides a separate, flexible area for application-specific data without affecting other partitions.
Components of Active Directory
| Logical Components | Physical Components |
|---|---|
| Doamin | Domain Controller |
| Tree | Sites |
| Forest | Networking Devices |
| OU | |
| Container | |
| Global Catalogue |
Active Directory services
Active Directory has multiple services, but the main one is domain service. Apart from that it has AD LDS, Certificate Services, LDAP, AD RMS and more.
What are the Key Features of Active Directory Domain Services?
Domain Services: Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) stores directory data, such as user accounts, groups, and devices, and manages communication between users and the domain controllers (DCs) in a network. It handles authentication and authorizations well.
Certificate Service: It is used to manage certificate-related activities like digital certificates, signatures, and ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of data through public key cryptography. By providing digital certificates, it enables secure information exchange over the internet and within an organization’s network..
Active Directory Federation Services: Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) enables Single Sign-On (SSO) authentication across multiple applications, domains, networks, and organizations. SSO allows users to securely access various resources, such as applications and websites, using a single set of credentials. ADFS authenticates users once and grants them access to all connected systems without requiring repeated logins, streamlining the user experience while enhancing security.
Rights Management: It controls who can access specific resources, such as files and emails, and determines what actions can be performed, such as viewing, editing, or sharing the data. By applying these policies, Rights Management ensures that sensitive information is protected and access is granted only to authorized users.
Features in Active Directory
Domain: To organize Active Directory objects logically, Microsoft introduced the concept of a Domain, which shares the same Active Directory database. It holds a copy of the Active Directory (AD) database and replicates any changes made to other Domain Controllers. This is how AD keeps its data up to date. It is responsible for Authentication & Authorization.
Tree: It is a combination of one or more than one domain. A tree can be viewed as a trust relationship. Domains within a tree trust each other and allow secure communication. A tree is part of a larger structure called a forest, and all domains within a tree share the same name space.
Forest: A forest is a collection of trees that share a common global catalogue, directory schema, logical structure, and directory configuration. The forest represents the security boundary within which users, computers, groups, and other objects are accessible. A forest allows for centralized management of resources while maintaining isolation between different forests.
Schema: Active Directory defines the types of objects (such as users, groups, and computers) and their attributes (like name, email, and security settings) within the forest. It acts as a blueprint that dictates how data is stored and organized across the directory.
Organizational Unit: OU is a container that holds other Active Directory objects like users, computers, printers, shared folders, and even other organizational Units. OU is unique in every domain.
Container: Containers are similar to OU, but group policies are not applied or linked to the container object.
Global catalogues: The global catalogues server is a domain controller that stores a complete copy of AD object attributes and a partial copy of all object attributes of all other domains.
Also Read AD DS Benefits: What Are the 5 FSMO Roles in Active Directory? Explain
Domains and Workgroups
| Features | Domain | Workgroup |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A centralized network structure where computers are managed by a server (Domain Controller like Active Directory) | A decentralized network structure where each computer manages its own settings |
| User Authentication | Centralized, uses Domain Controller for authentication and security policies | Local, each computer has its own set of users and passwords |
| Security | Higher security | Lower security |
| Scalability | Scalable, suitable for large networks and enterprises | Limited scalability, best for small networks |
| Resource Sharing | Resources (files, printers) can be shared across the domain and managed centrally | Resources are shared locally on each computer, no central management |
| User Access | Users can log in to any computer in the domain with the same credentials | Users can only log in to the computer where their account is created |
| Administrator Control | Centralized admin control, can enforce group policies across the network | Admin control is local to each machine, no group policy enforcement |
Lets learn more about AD DS setup process in FAQ.
Active Directory FAQs
Is there any alternatives of Microsoft Active Directory?
There are other directory services that offer similar features to Active Directory (AD) include Red Hat Directory Server, Apache Directory, and OpenLDAP.
- Red Hat Directory Server manages user access in Unix environments. Like AD, it uses user IDs and certificates to control access to directory data.
- Apache Directory is an open-source tool that works with any LDAP server and supports systems on Windows, macOS, and Linux. It includes a schema browser and LDAP editor, along with Eclipse plugin support.
- OpenLDAP is an open-source LDAP server mainly used in Windows environments. It lets users browse, search, and manage directory objects, and supports features like schema browsing, password management, and LDAP SSL (Secure Sockets Layer).
What is LDAP?
LDAP is a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol used to access and manage directory services. MS AD uses LDAP protocol for communication between clients and servers. Check out below how LDAP is different from MS AD:
What Is LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) & Workflow?
What is a Group Policy?
Group Policy in Active Directory allows administrators to enforce specific settings and configurations on users and computers across the domain. Policies can include security settings, desktop configurations, and software installations.
What is a Active Directory different from Azure Active Directory?
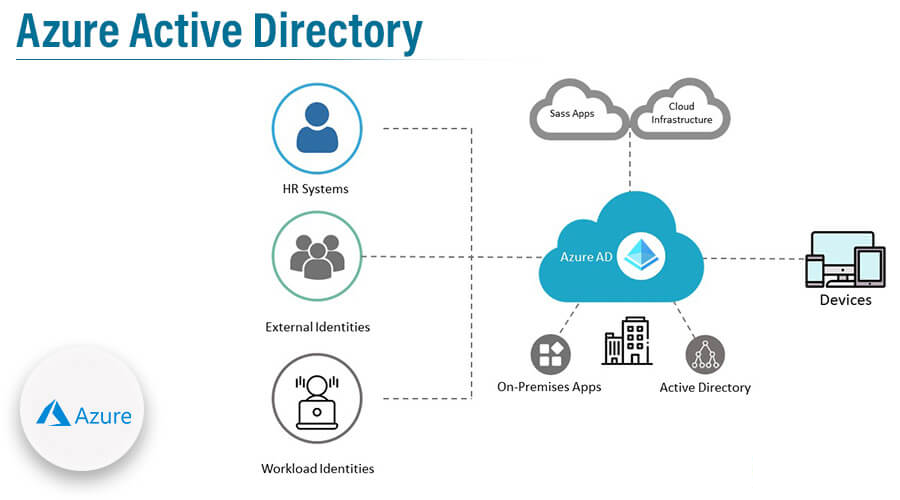
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) is a cloud-based identity management service by Microsoft that controls access to SaaS applications like Microsoft 365 (Office 365), custom apps on Azure, traditional enterprise apps, and on-premises resources.
It supports features such as just-in-time access, multi-factor authentication, password less login, mobile device management, and identity federation standards like SAML and OAuth2.

